As required in the era of digital transformation, companies need to ensure accurate planning and real-time control of processes and resources in order to succeed. For this purpose, a business can implement an ERP system. What is ERP, what are its benefits for businesses and how is it created? Read on to find out.
What Is ERP?
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning.
An ERP system is an integrated platform for managing large amounts of data in the production and supply chains. The system is divided into numerous modules that handle finance, accounting, procurement, human resources, manufacturing and delivery, which allows businesses to encompass and automate all processes.
Modern ERPs are more than just the integration of services. They incorporate artificial intelligence, cloud computing, Big Data analytics, IoT technology, and so on, to boost productivity.
Leverage SaM Solutions’ decades-long expertise in IT to develop high-quality custom software for your business.
In a Market Research Future report on the global ERP software market, it’s been predicted that the market will grow from $32 billion in 2017 to $49 billion in 2023, at a CAGR of 7%. North America is expected to dominate this segment.
ERP Benefits and Drawbacks
What is the main driver for the growth of this market? Simply put, it’s the desire of organizations to increase their process transparency and operational efficiency.
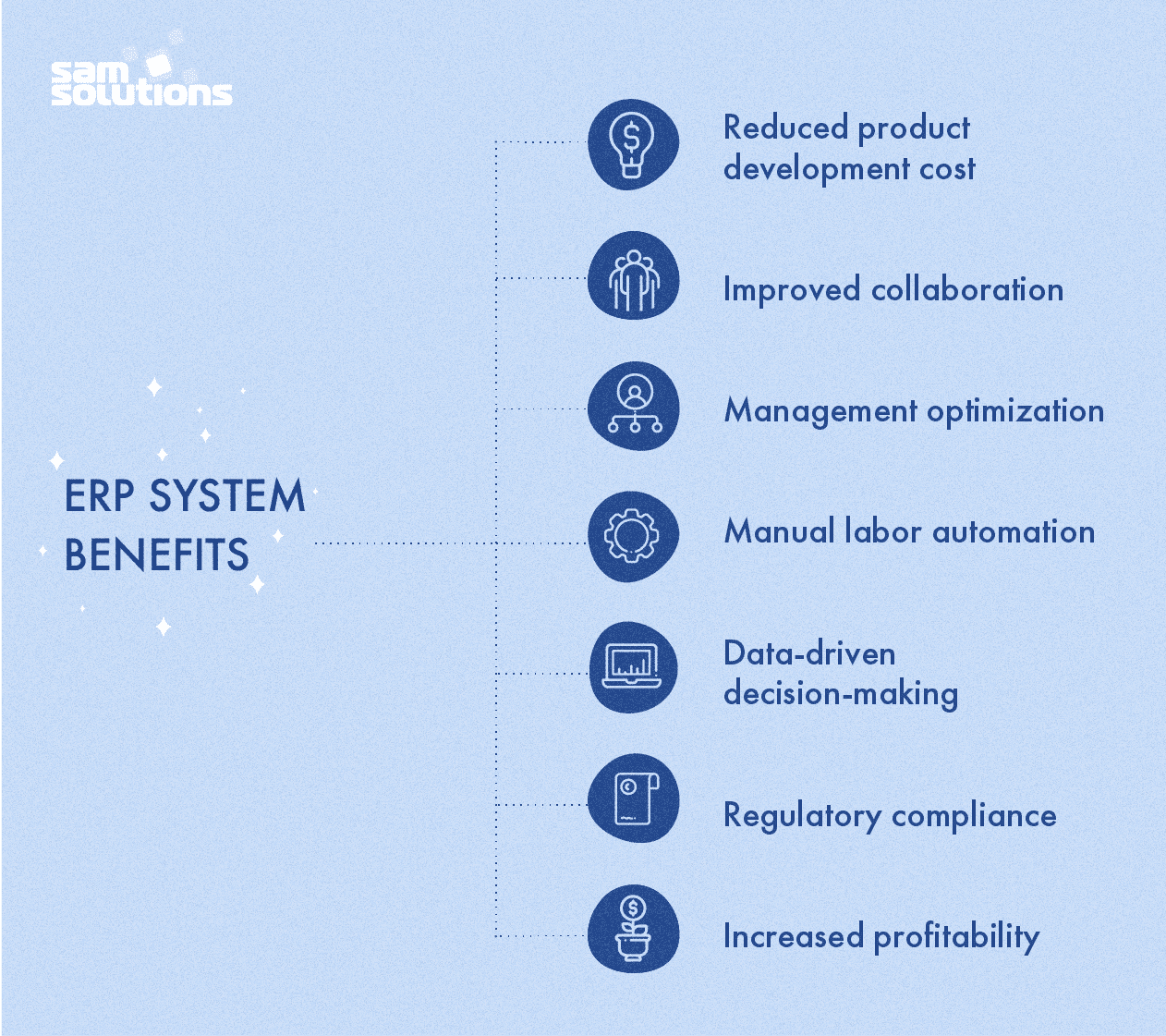
The ERP system implementation requires a considerable amount of time, financial expenses and the engagement of all departments within the company. Such enormous effort to create the right enterprise resource planning solution pays off with numerous benefits:
- Reduced product development cost — effective management and quality assurance systems minimize errors and risks.
- Improved collaboration — information barriers between departments are eliminated as there is a single database.
- Management optimization — all processes are controlled via a single center, so no issue can be missed.
- Manual labor automation — smart digital technologies incorporated into ERPs replace humans in many operations.
- Data-driven decision-making — real-time data analysis allows managers to make decisions quicker.
- Regulatory compliance — specialized automated systems are taught to monitor compliance of produced goods with relevant rules and standards.
- Increased profitability — the above-mentioned benefits together provide full enterprise visibility and efficient operations, helping reach the common goal of enhancing the output.
There are a few drawbacks that come with the migration to enterprise resource planning:
- The high costof implementation and maintenance (the more modules are needed, the more expensive the system is)
- A complicated integration processthat requires a compatible business environment and full engagement of all the teams
Simply put, an ERP solution is a significant investment of time and money, and if you manage it properly, it will be worth it.
Industries That Need ERP Software
If you look at most industries, their general working processes are similar and connected with supply chain, customer relationships, internal communication, accounting and finance control, marketing and production. Consequently, any industry can be managed by a typical software solution with a portion of customization.
There are integrated enterprise resource management applications available in the market for almost all kinds of industries. The most involved are:
- manufacturing
- healthcare
- hospitality
- retail and wholesale
- construction
- transportation and logistics.
ERP’s Interior
Typically, enterprise resource management software has a modular architecture, meaning that workers can access only those modules of the system that concern their duties, while top management can both review data and make changes within the entire system. By keeping to a modular approach, companies enhance security and get more accurate data at all levels.
Functionality
In general, ERP modules perform the following functionality — all from the single platform:
- Order processing
- Production management and manufacturing resource tracking
- Supply chain management
- Customer relation management
- Content management
- Human resources management
- Partnership and deal management
- Financial management
- Marketing
- Analysis and reporting
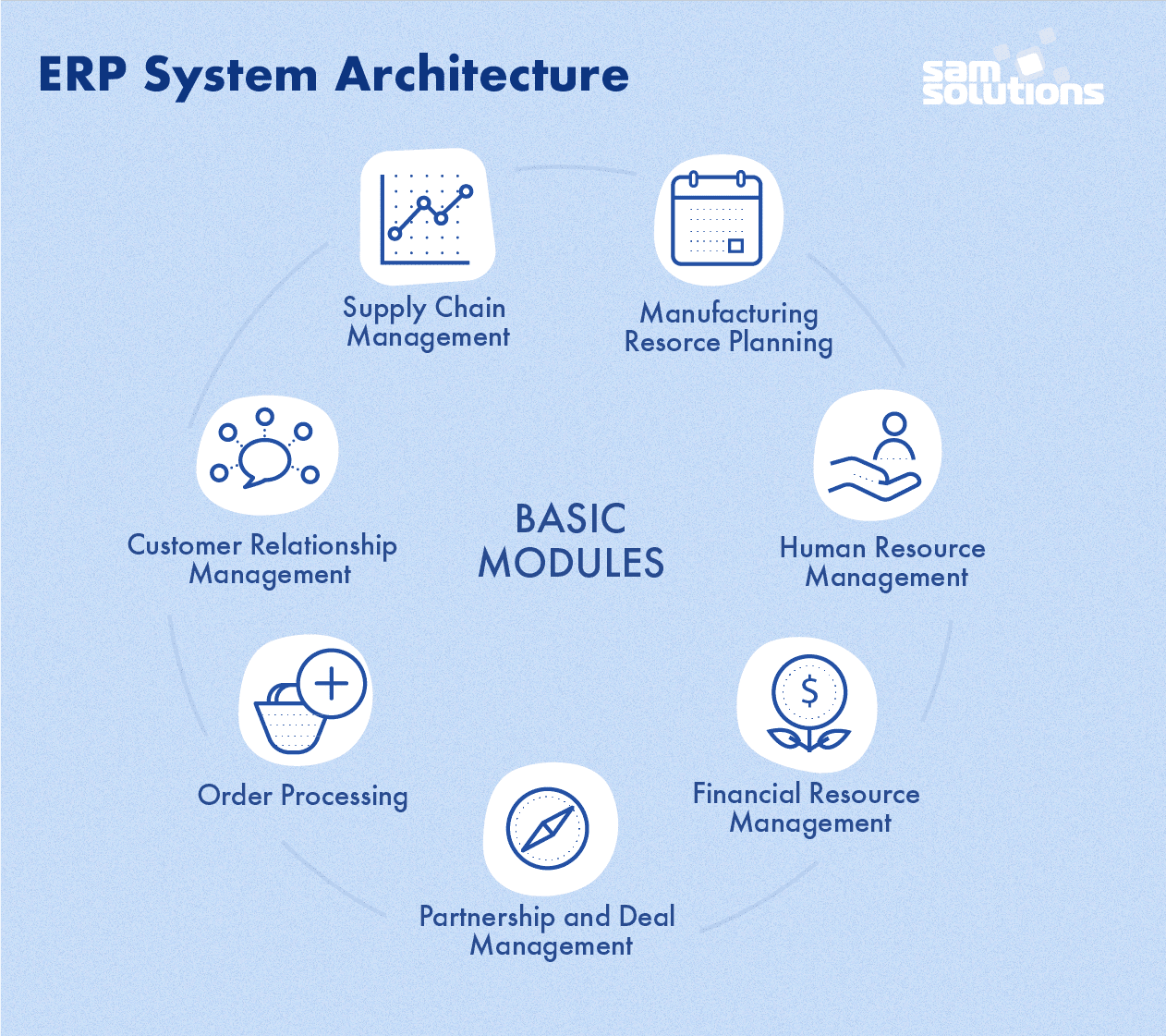
These are only basic examples, and a specific business most probably requires other modules.
Must-Have Capabilities
ERP applications can be loaded with a variety of tools and features, depending on the industry. Let’s look at the must-have features for creating efficient software.
Hosting Options
Depending on business specifics, companies have different flexibility needs and security requirements, so they should be free to choose where to store their data. A proper enterprise resource planning system should provide all possible options, such as:
- on-premise servers
- cloud storage
- hybrid integration platforms.
In this case, companies can decide for themselves what works best for them while having no limitations concerning access, needed space, data protection and maintenance price.
Easy Integration
Because of the modular structure of ERP platforms, they usually incorporate various function-specific solutions, such as CRM and CMS systems, supply chain management, financial, HR management, marketing, manufacturing resource planning and other modules. To avoid silos, such platforms require proper integration of their stand-alone parts, which will enable a holistic overview of all systems and their well-coordinated operation. This also enables an easy and quick migration or updating process.
Scalability
An ERP system should be scalable to meet the growing requirements of businesses, and easily adapt to any future needs. Otherwise, companies may face problems within a couple of years and will have to either start the process from the very beginning or introduce additional applications, complicating the whole system.
Mobile Compatibility
“Mobile-ization” is a common trend across all industrial sectors. An ideal ERP product is one that allows teams to access a single platform from any device — smartphone, tablet, laptop or desktop.
There are two ways for companies to acquire their own efficient ERP software solutions — getting an out-of-the-box solution followed by its adjusting to a company’s needs, or creating custom ERP software. Read on to learn more about these methods.
Out-of-the-Box ERP Software
Following this method, a company purchases a ready-made offering provided by ERP vendors, and customizes and then uses it within its infrastructure. This option is, undoubtedly, a time-saver, which can be a significant benefit for many businesses. Another advantage is its cost-effectiveness, because the initial expenses for purchasing a ready-made product are lower than those for developing a system from scratch.
The biggest disadvantage of boxed apps is their inability to satisfy all the specific company requirements and to seamlessly integrate into the company’s infrastructure.
There are hundreds of ERP software providers available on the market, but companies need to remember that it’s their requirements and needs that should determine their choice of ERP software. We’ve selected a few good examples of enterprise resource planning systems — big names that are featured in 2019 Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Cloud Core Financial Management Suites for Midsize, Large and Global Enterprises.
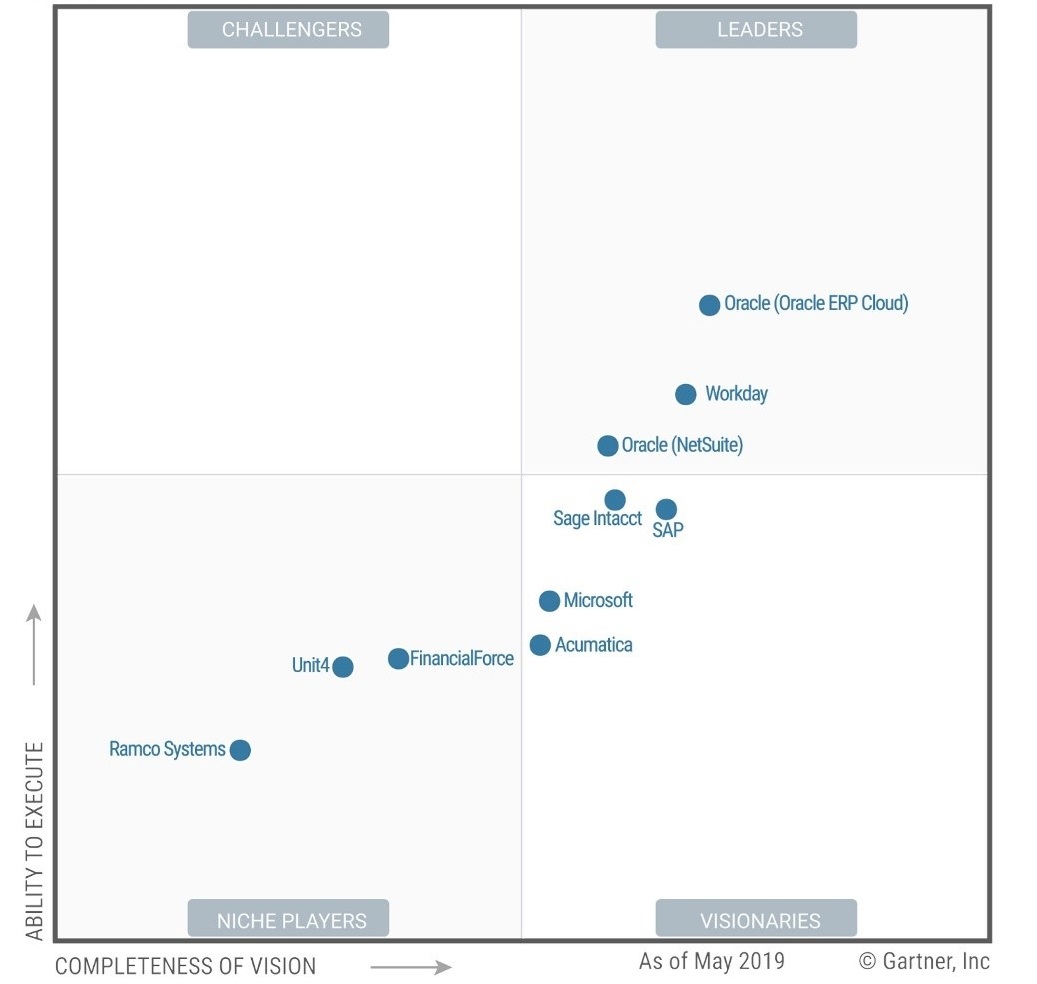
Source: oracle.com
Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Resource Planning
The core strength of this comprehensive solution by Oracle lies in its robust financial functionalities that enable advanced analytics and reporting. Companies that use these insightful analytics in addition to the Intelligent Procurement Cloud tool are able to efficiently control and reduce their expenses.
The core functionality includes the following modules:
- Financials
- Project management
- Procurement
- Risk management
- Enterprise performance management (EPM)
- Supply chain management
- Adaptive intelligent apps for ERP
- Analytics for Cloud ERP
Businesses of all sizes can also benefit from scalability ensured by Oracle’s cloud deployment model. Moreover, using the Risk Management tool enriched with AI-powered algorithms, companies can control practically all potential risks.
Oracle NetSuite ERP
More than 40,000 companies from various industries globally choose NetSuite because of its high quality, outstanding capabilities and facilitation of 360-degree visibility and control of company operations. The solution has the following functionalities:
- Financial management
- Financial planning
- Order management
- Production management
- Supply chain management
- Warehouse and fulfillment
- Procurement
The NetSuite ERP features embedded business intelligence, ease of customization, scalability and support.
SAP S/4HANA
This powerful, intelligent ERP system comprises tools and solutions for practically all business processes. SAP is a pioneer of enterprise resource planning systems — since 2004, the solution has supported 50,000 customers in 25 industries. With this ERP suite, companies get end-to-end support for all business activities.
The SAP S/4HANA suite can be deployed either on-premises or as a cloud-based ERP solution (in a public, private or hybrid cloud). It relies heavily on embedded AI, machine learning and advanced analytics, in-memory database and a simplified data model.
Microsoft Dynamics GP
The ERP solution by Microsoft is built on the principles of simplicity and functionality, which is why its interface is easy to learn and use. Microsoft Dynamics GP provides a wide range of customization options and a high level of security.
Quick configuration and easy data migration from third-party sources are handled by the RapidStart Services feature. Moreover, MS Office apps and SQL databases serve as the basement for Dynamics GP, providing smart reporting and business intelligence features.
The Microsoft ERP suite includes the following modules:
- Financial management and accounting
- Inventory management and operations
- Sales and service
- Human resources and payroll
- Business intelligence and reporting
Developing a Custom ERP: Step by Step
Developing a custom enterprise resource planning system is complicated but is definitely worth it: it provides ideal compatibility with the company’s processes.
The core benefit of a customized ERP system is that it is developed exclusively for the company’s needs, so a company gets software that perfectly suits its organizational strategies and operations. Such a system doesn’t have integrational problems and provides the best execution of your business functionality.
The main drawbacks are the cost and time of development. To create such a solution from the ground up, a business needs a professional team of developers, designers and testers, a long timeframe and high initial investment. But in the long term, the project will be cost-effective, with fewer risks and a high ROI.
Let’s take a look at the stages of the ERP system building process.
1. Understanding Business Processes and Defining Goals
Software creation begins not with coding but with understanding the client’s business.
Complete visibility of the company is the result of meetings and negotiations. Clients should explain their requirements, wishes and expectations regarding the functionality of the product they want created for them.
2. Blueprint and Prototype Creation
The team pays particular attention to the prototype.
At this stage, one has to decide on the modules that the system will contain. The most common modules are manufacturing, HR, procurement, sales, financial and customer relationship management. Other services and functions can be integrated into the system as well, depending on the client’s requirements.
3. Development
At this stage, technical decisions should be made regarding:
- hosting (on-premises or cloud)
- backend (databases, architecture, security systems, content management and other components that make the software work, update and change)
- frontend (UI and UX)
- integration (important information is not to be lost, but should be reconfigured to be available for further usage in a new software structure).
4. Testing

The team performs different types of testing: unit, integration, system, functional, security, etc. In the end, engineers check if the software meets all the initial requirements and is comfortable to work with. After this, the system can be implemented and accepted by the client.
Plan Your Resources Properly with ERP
The essence of enterprise resource planning systems is in breaking barriers between company departments for more efficient performance. This philosophy is actively adopted by organizations, so we can find this type of software practically in any industry. A successful ERP software is half the battle for the successful operation of a business, as it can streamline processes, reduce costs and provide visibility and transparency.
Contact us to learn how an ERP system can become a source of competitive advantage for your business. We are ready to build or tailor an enterprise resource planning app for your particular needs.



























 5 Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce Application
5 Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce Application Using Salesforce to Improve Your Sales Pipeline: Five Tips
Using Salesforce to Improve Your Sales Pipeline: Five Tips Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Five Best Frameworks
Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Five Best Frameworks How to Develop Custom Accounting Software
How to Develop Custom Accounting Software 10 Best Web Development Frameworks in 2024
10 Best Web Development Frameworks in 2024










 Top 30 Ecommerce Tools to Elevate Your Business in 2024
Top 30 Ecommerce Tools to Elevate Your Business in 2024 5 Best Tools to Improve Embedded Software Testing
5 Best Tools to Improve Embedded Software Testing Why React and Node.js Are the Top Technologies for Creating High-Performance Web Apps in 2024
Why React and Node.js Are the Top Technologies for Creating High-Performance Web Apps in 2024 10 Best IoT Platforms for 2024
10 Best IoT Platforms for 2024
Thank you so much! I gather lots of knowledge from this article. However, An ERP system can streamline your entire association and put your data each in one place, enabling more accurate reporting and a more effective, collaboration- grounded and data- driven work terrain.. So Highly recommend it to all who read this article who wants to develop their career on ERP Software. Thanks again and waiting for the next article.
Good article, but it did not go deep in the topic of ERP development as it missed to address what I am looking for in terms of information about the degree of looseness, separation, and dependency between modules, and how to derive the variables that can represent settings or customization configuration in the ERP system.
Enterprise resource management software typically has a modular architecture, meaning that workers can only access those modules of the system that concern their duties. This enables companies to enhance security and get more accurate data at all levels. Additionally, top management can both review data and make changes within the entire system.
Thanks for the article about ERP development! I have been looking for such information for a very long time!
You is one of the best Erp Software Development Company In US! You develop software on customer basics to generate maximum profits and also innovate new ideas to increase the leads!
Great Blog! Such a complete guide to know well about ERP and its benefits. Thank you for sharing this informative article. Keep sharing !