In a short period of time, cloud computing has shifted from a buzzword to a robust technology vectoring the present-day IT domain. For many reasons, cloud software development is promising for companies regardless of their industry focus.
This article provides important facts and essential aspects of cloud computing and discusses its benefits and challenges for businesses.
Drive your digital transformation to the next level with our world-class cloud development services
What Is Cloud Computing?
The term cloud computing encompasses a range of services delivered over the internet by providers.
Cloud-based refers to computing resources (servers, storage, networking), tools (runtime, OS, middleware) and ready-made solutions (analytics, monitoring) that users can access on demand.
Cloud-based development means that you don’t need to build and maintain your own physical infrastructure (servers or data centers) or install development tools to create software. Instead, you can utilize technology services and computing power provided by third-party vendors.
Cloud Computing Facts and Statistics
History:
- 1961 – The idea of utility computing (which is the essence of the cloud) was formulated.
- 1996 – The term cloud computing was coined.
- 1999 – Salesforce became the first company to offer applications over the internet, thus introducing Software as a Service (SaaS).
- 2006 – Amazon launched Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), the first Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) platform.
Current stats:
- In 2023, Statista’s data shows that Amazon Web Services (AWS) leads the cloud provider market with a 32% share, followed by Azure at 22% and Google Cloud at 11%.
- The US is the undisputed leader in cloud adoption.
- Financial services, transportation and logistics, media and entertainment, and healthcare are among the industries at the forefront of embracing cloud technologies.
- According to Gartner’s latest forecast, global spending by end-users on public cloud services is expected to increase by 21.7%, reaching a total of $597.3 billion in 2023, compared to $491 billion in 2022.
- Gartner also predicts that by 2026, approximately 75% of organizations will adopt a digital transformation model built upon the cloud as its essential foundation.
Cloud Computing Features
- Remote servers. Cloud solutions use servers in faraway data centers.
- Provider takes care. The provider looks after the servers and keeps them running; you don’t have to.
- Pay as you go. You pay only for what you use, like how you pay for your phone.
- Anywhere access. You can use remote services from any device and anywhere.
- Flexible scaling. The cloud can get bigger or smaller depending on what you need. No worries about getting more storage or keeping things you don’t need.
- No downloads. You don’t have to download and install special software on your device.
On-Premises vs. Cloud Solutions
Cloud hosting has become an excellent alternative to the traditional approach, which typically means there is the on-prem IT infrastructure within a company.
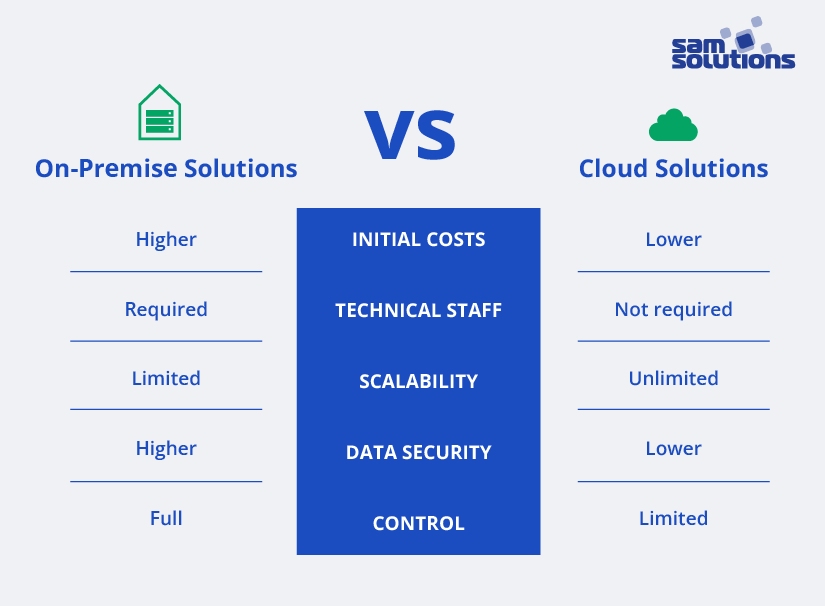
When deciding between on-premises and remote solutions, you should consider these factors:
- Budget: Setting up in-house infrastructure involves substantial upfront costs, while cloud hosting is more cost-effective.
- Technical expertise: On-premises solutions require a dedicated technical team for maintenance and support. With cloud solutions, the provider handles these tasks, saving you the hassle.
- Flexibility and scalability: If your business is likely to grow, cloud storage can easily expand as needed. The expanding on-premises infrastructure is more complex as it involves purchasing and deploying additional servers. However, if your project won’t change in size, on-premise infrastructure could be suitable.
- Control level: If you require complete control over both hardware and software, owning your infrastructure is the way to go. In contrast, cloud hosting limits access to hardware and some operations.
- Security Needs: Keeping everything within your company can enhance data security. Cloud storage and processing don’t guarantee absolute protection, especially in public platforms, where breaches and data leaks are possible. However, it’s worth noting that private cloud providers are making significant strides in improving data security.
Web-Based Apps vs. Cloud-Based Apps
The terms web-based and cloud-based are often used interchangeably, but not quite correctly so.
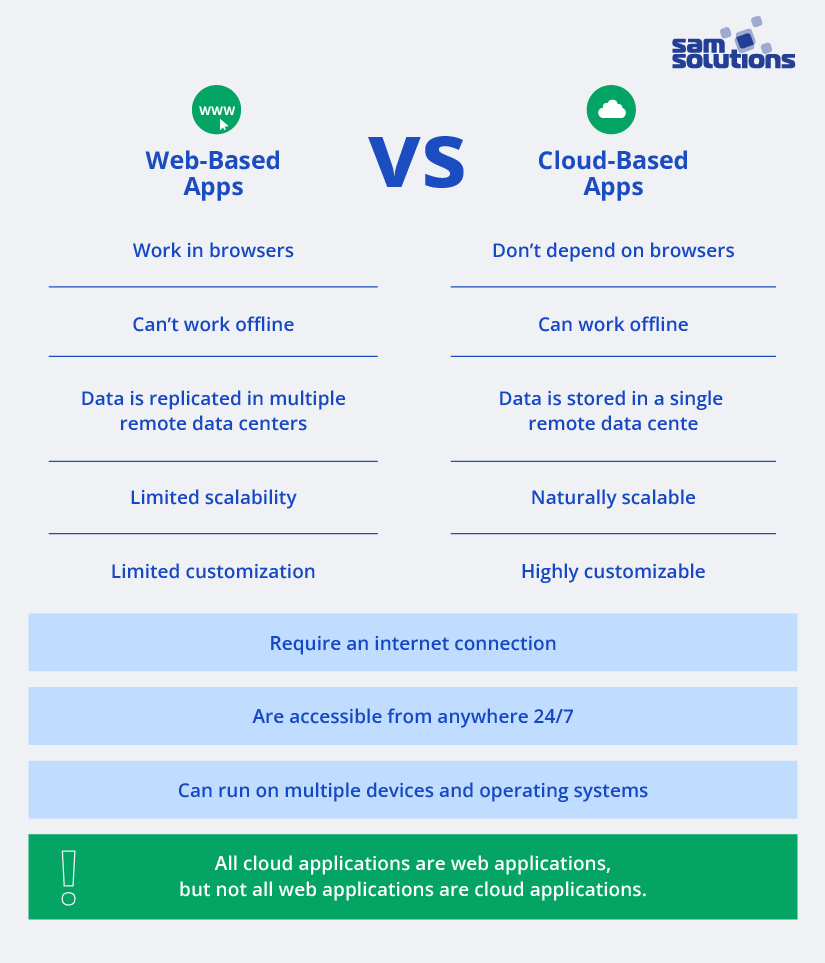
Since cloud apps are an advanced version of web apps, they share some similarities:
- Both types of solutions require an internet connection to access services.
- They are accessible from anywhere 24/7 and can run on multiple devices and operating systems.
- All cloud applications are web applications, but not all web applications are cloud applications.
There are also some important distinctions between them:
- Web apps run on web browsers only, while the function of cloud apps doesn’t depend on browsers (you can access them via a web browser or install them on mobile devices).
- Web-based solutions need a continuous internet connection. Cloud-based solutions can work offline because they can cache data locally and synchronize it when the connection is restored.
- Cloud solutions use multiple remote data centers; web apps utilize a single remote data center.
- Features and functionality of cloud apps are easily scalable; the scalability of web apps is limited.
- Cloud apps offer a high level of customization to users and developers. Web apps are not highly customizable.
Social media websites, online banking and eCommerce stores are good examples of web-based solutions. Dropbox, Slack and Gmail are some typical cloud-based solutions.
Cloud Models: Public, Private, Community, Hybrid
There are four basic cloud deployment models: public, private, community, and hybrid. Each model has its advantages and disadvantages. To choose the right model for your project, you should consider a range of factors such as the number of users, privacy concerns, budget and more.
Public clouds are shared resources that multiple users can access simultaneously. They do not allow sophisticated customization but do provide high scalability and fast implementation at a reasonable price. The drawback of this model is a possible vulnerability in terms of data privacy. Choose this form of software if:
- Lots of people use your application.
- Your projects require team collaboration.
- Your vendor has a well-established security policy.
- You need additional capacity for peak times.
Private clouds are not available to the public. They are designed for the needs of a specific company and its exclusive use. While such solutions are quite costly, they provide a more individual approach, enhanced customization and better data control. The private model suits you if:
- Your organization requires a high level of security and data protection.
- Your project is continually changing and growing.
Note! Some companies dealing with public cloud technologies offer a private version and vice versa, so you can develop cloud-based personal software as well as a public version while working with a single provider.
Community clouds provide the ability to share infrastructure, data, and resources between several organizations.
This deployment model is perfect for multiple companies that want to collaborate within one domain (e.g., healthcare).
The hybrid cloud is a mix of the two previous models. This model includes both public and private options and provides different control levels (external and internal). The hybrid cloud is convenient because you can choose the most suitable environment for each aspect of your business. The drawback is that you must keep an eye on all of them simultaneously to ensure that the whole process is in order. The cost is also higher.
You may use a hybrid approach if you provide services for numerous clients, and a public cloud is necessary to interact with them, but data security is of high importance and should be kept within a virtual private network.
Types of Cloud Services
As mentioned, providers deliver a range of services, from storage to ready-made solutions. Hence, there are three basic models: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
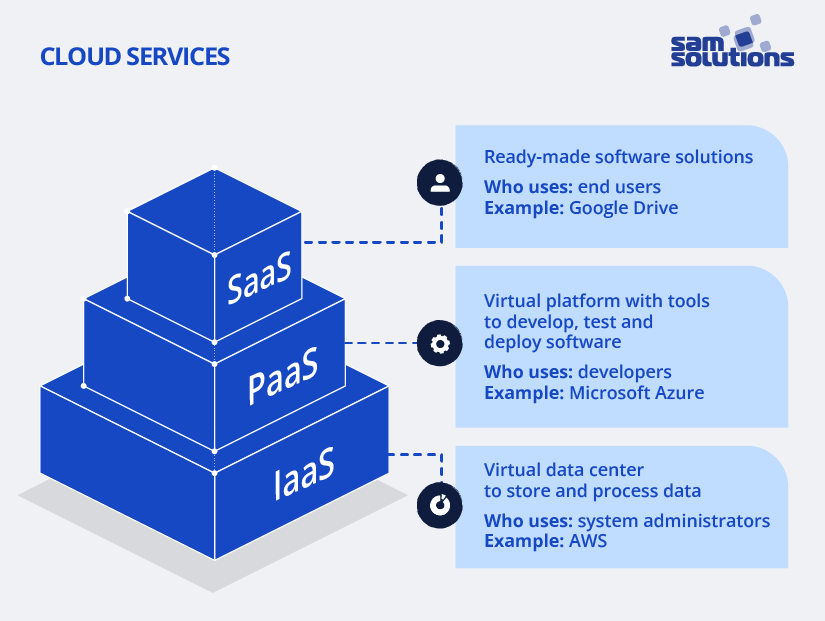
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) delivers computing resources (servers, storage, networks) using virtualization technology. In other words, IaaS is a virtual data center that replaces physical hardware.
- System administrators work with IaaS: they install and maintain operating systems, runtime, middleware, and applications.
- Examples: AWS, VMware
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a virtual software development platform.
- Developers work with PaaS: they use built-in tools to create, test, launch and customize applications. With this model, customers focus on their app development, not on infrastructure maintenance.
- Examples: Microsoft Azure, Heroku
Software as a Service (SaaS) is the delivery of ready-to-use software solutions.
- End users leverage SaaS products to complete tasks such as communication, storage, and analytics.
- Examples: Office 365, Google Drive
The world’s list of cloud providers is topped by Amazon Web Services (AWS), followed by Microsoft Azure, Google, IBM, Alibaba, and Oracle.
However, when choosing a solution, one should not be limited to big market players. Backed up by rich cloud computing expertise and a significant number of successful projects, SaM Solutions has created its own PaaS — SaM CloudBOX. This private platform relies on DevOps best practices to help businesses jump-start their software development projects.
Cloud Software Development Advantages
A growing number of organizations opts for cloud migration. The following are some factors that influence the adoption of cloud computing and the growth of this market.
- Cost efficiency. Cloud-related costs are lower than those of desktop software; the variety of payment options, such as pay-as-you-go, one-time payment, and others, allow users to significantly cut software maintenance expenses. Also, this approach eliminates the need to invest in on-premises hardware and removes license fees.
- Extended flexibility. Remote services allow you to easily and quickly scale up and down your system’s capacity.
- Rapid deployment. The deployment of a system in remote data centers is time-effective as it may take only a few minutes.
- Unlimited storage capacity. Cloud technology does not limit a company’s storage space or compel it to extend it, unlike desktop software.
- Facilitated disaster recovery. The remote backup and recovery processes are much more streamlined than the same processes on a physical device.
- Automated software integration and updates. Cloud computing enables automated software integration and updating and allows users to skip additional optional configuration and customization.
- Improved team collaboration. You can unify resources and enable team members to access the information from any place. This facilitates collaboration and streamlines processes within a team.
Cloud Software Development Challenges
Like any process, adopting cloud software can come with obstacles and risks. Here are some key considerations:
- Compatibility. Not all workloads can smoothly transition to the cloud, especially if they rely on outdated platforms, have limited internet bandwidth, require intensive CPU and input-output capacity, or have an incompatible structure. Additionally, it’s crucial for remote software to align with a company’s policies, needs, and existing technological infrastructure.
- Technical challenges. Just like any system, the cloud is susceptible to outages and other technical issues. Maintaining high technology standards doesn’t guarantee immunity from these problems.
- Security concerns. Entrusting sensitive data to a third-party service provider can potentially compromise the security and safety of that data. Also, this potentially increases the chances of hacker attacks.
The Basics of Cloud Migration
If your company is considering moving its workloads to the cloud, here is the checklist to help you do so with maximal efficiency.
Planning
Proper preparation and planning is half of the success. Consider the following aspects to develop your migration strategy:
- Prioritize workloads that will be moved to the cloud. We suggest starting with the less critical ones. This helps minimize risks in case of any issues or system malfunction.
- Check the software architecture. Examine if the current architecture requires modifications against the new remote environment, as it differs significantly from the on-premises environment.
- Investigate how the migration will influence the workload’s performance. There must be positive changes in performance. If your investigation shows no changes or even negative changes, figure out the reason. It may turn out to be that in this specific case, migration is irrelevant. If you are still sure that your workload can be moved to the cloud, check your strategy for possible pain points.
- Explore how the application or database downtime will affect customers’ businesses.
- Develop an algorithm for updating, troubleshooting, performance assessment and other routine matters.
- Prepare your staff for the adoption of new technology.
- Develop a security policy.
Migration
Gartner defined five approaches to the migration process:
- Lift and Shift. This is like picking up your application as it is and moving it to the cloud without making significant changes. It’s like moving your house to a new location without renovating it.
- Refactoring. This approach involves making some adjustments to your application to better fit the cloud environment. It’s like renovating your house to make it more modern and efficient.
- Re-platforming. Here, you adapt your application to the cloud platform’s specific services and features. It’s similar to customizing your house to fit a new neighborhood’s style.
- Rebuilding. This means creating your application from scratch in the remote environment, taking advantage of cloud-native features. It’s like demolishing your old house and constructing a new one.
- Replacing. Instead of moving the application, you choose a completely different cloud-based application or service that serves the same purpose. It’s like selling your old house and buying a new one in a different location.
Nowadays, companies alter and/or mix these principles to fit the specific business requirements.
Verification
After the application has been migrated, check the following:
- Does the application work?
- Have you moved all the data?
- Can users access it?
- Do all the internal software components communicate properly?
- Can an admin monitor the application’s performance and manage it?
Ideally, an automated testing strategy helps estimate whether the migration was successful or not. If you cannot apply automated verification, try to do it manually.
We develop innovative cloud-based solutions for clients around the world
Get Ready for a Shift
We are witnessing a steady growth in the popularity of cloud solutions across countries and industries. For most companies, the move from on-premises IT landscapes to a hybrid or full cloud model is inevitable.
SaM Solutions highly recommends turning to subject-matter experts for software development or migration, as only professionals can successfully complete the journey to the cloud.
We have a track record of successful cloud-based projects. Working with our experienced programmers and consultants, you will have access to all the necessary information and will be able to decide on the exact model while staying within the budget.



















 The Latest 15 Information Technology Trends in 2024
The Latest 15 Information Technology Trends in 2024 Top 10 Embedded Software Development Tools
Top 10 Embedded Software Development Tools IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: What’s the Difference?
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: What’s the Difference? IoT Development: Top 15 Internet of Things Tools and Platforms in 2024
IoT Development: Top 15 Internet of Things Tools and Platforms in 2024 10 Examples of Predictive Analytics
10 Examples of Predictive Analytics













 MACH Technology: What Is It?
MACH Technology: What Is It? The 16 Best .NET Development Tools
The 16 Best .NET Development Tools How to Create Your Own CRM System: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Create Your Own CRM System: A Step-by-Step Guide How to Create Artificial Intelligence Software
How to Create Artificial Intelligence Software The Ultimate Guide to Conducting an Audit of Your Ecommerce Website
The Ultimate Guide to Conducting an Audit of Your Ecommerce Website
Very informative!!
Hello there, I thoroughly enjoyed your article, I wanted to write a little comment to support you and wish you a good continuation All the best for all your blogging efforts.
Keep working, great job!
The tendency of migration from on-premise and cloud models is growing, and it is also related to SaaS app development. Thanks, good article.
Ahaa, its good dialogue about this article, I have read all about cloud software development, so now me also commenting here.
You can not imagine just how much time I had spent for this info!
Thanks!
Keep up the superb works, I’ve included you guys to my own blogroll.
I could not resist commenting. Perfectly written!
I wanted to thank you for this good read!! I certainly enjoyed every bit of it.
I’ve got you book-marked to check out new things you post…
Hurrah! After all I got a webpage from where I know how to genuinely get valuable information regarding my study and knowledge.
You are amazing! Thanks!
Great read! Thank you.