The Internet of Things is no longer an experiment. It is penetrating all vertical markets, promising new opportunities both for customers and service providers.
With the increased demand for smart technologies and connected devices, the future of IoT looks promising. We’ve compiled the main IoT trends and predictions based on experts’ opinions and statistics.
Leverage the latest IoT technologies with our expert team and get powerful IoT solution for your business.
IoT infrastructure has the greatest potential to integrate the physical and digital worlds and create new revenue streams and business models.
Here is a list of predictions for the industry development:
- The number of connected devices worldwide will continue to grow, impacting different areas of life.
- Technologies such as artificial intelligence or blockchain will merge with the Internet of Things, creating new solutions.
- Specialized platforms, connectivity options and data processing methodologies will be needed.
- The growing IoT ecosystem will become vulnerable to hacking attacks like never before, so vendors will have to prioritize IoT security solutions.
1. Connected Devices Here, There and Everywhere

One of the most obvious and realistic IoT predictions is that the number of connected devices will continue to increase over the coming years. According to Gartner, there were 6.4 billion IoT units installed worldwide in 2016. By the end of 2018, this number should exceed 11 billion connected units. Gartner’s long-term forecast depicts up to 21 billion things connected to the internet by 2020.
Real and foreseen spending on the Internet of Things is also impressive. It will constitute $772.5 billion in 2018, based on IDC research. Worldwide IoT spending is forecasted to sustain a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.4% through the 2017-2021 period, surpassing the $1 trillion mark in 2020 and reaching $1.1 trillion in 2021.
At present, the largest share of spending is devoted to the IoT hardware including modules, sensors and other infrastructure components. But the situation is predicted to change soon, with smart services and software being the fastest growing technology segment. By 2021, more than 55% of IoT investments will be into software and services including apps, platforms, data analytics and security.
The Internet of Things solutions market in the European Union in 2025 (in billion euros)
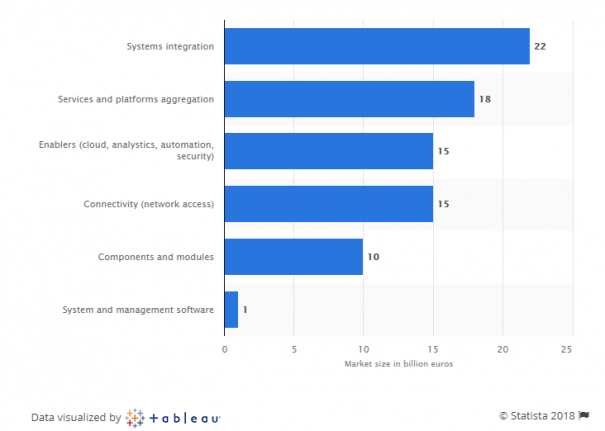
Source: Statista
2. Convergence with Other Technologies

IoT technology is insufficient and not fully flexible when used in isolation. It needs to mesh with other advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Big Data, blockchain, cloud and fog computing to gain greater profits from investments. Such unions have already been emerging.
We have seen the dynamic adoption of artificial intelligence to the enterprise processes in recent years that is leading to a higher level of automation. The future of IoT is inextricably linked with AI and Big Data, as the processing of huge volumes of data gathered by connected devices requires advanced analytics and needs to be automated.
For example, if a company implements IoT solutions augmented with AI and machine learning technologies, it will get a deeper and quicker analysis of real-time data streams, which will in turn improve the decision-making ability.
Blockchain is the innovation entering the mainstream at a quick rate. Blockchain adoption in IoT is expected to rise due to the fact that it provides the most secure data transactions and storage without the central control point or intermediaries. This technology is among the top Internet of Things future trends and is expected to play a crucial part in almost every industry in 2019 and beyond.
Cloud and fog computing (edge computing) will provide IoT with needed flexibility and accessibility, allowing to cut expenses on hosting services.
3. New Connectivity Options

Wireless connectivity is an integral part of the Internet of Things. There are numerous IoT connectivity options with various characteristics: bandwidth, power, range, network latency, the frequency and size of data exchange, the location of processing resources, cost, etc. These are local area networks (LANs), personal area networks (PANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
The traditional offerings are:
- Bluetooth (for very short-range connectivity)
- Wi-Fi
- Zigbee (low-power mesh networking technology)
- Z-Wave
- Thread
- LoRa
- Sigox
The choice of the connectivity option depends on the application requirements. Some apps need powerful infrastructure to process the intensive data stream, while for others, low data rates might be enough, but the wide-area connectivity is a must.
Providers tend to create new connectivity solutions and standards that will be able to address any issue of the ever-growing IoT ecosystem.
The future of the Internet of Things connectivity is in technologies such as:
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- 5G
- LPWANs
4. IoT Platforms

Any organization that intends to implement IoT into its products and services needs the integration system for remote monitoring and management of all devices. Specialized platforms are designed for these very needs.
The main trend for the coming years is developing IoT platforms, making them mobile and integrating them with cloud services. This will enable low adoption costs, quick deployment, global reach and minimal maintenance burden.
Smaller providers will definitely follow the global IT giants that have developed their IoT platforms: Amazon Web Services IoT Suite, Google Cloud IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT Suite, SAP Cloud Platform for the Internet of Things, and others.
5. IoT Gets Practical

Among the top Internet of Things predictions, there is a stronger fragmentation of the technology according to its practical applications in various industries. Different categories of the IoT are already in existence:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Automotive Internet of Things
- The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- The Internet of Things for the smart city and smart home
The practical usage of connected devices will expand to other industrial and social areas, creating new IoT categories.
IDC forecasts that the top three industries in terms of IoT spendings in 2018 will be manufacturing ($189 billion), transportation ($85 billion) and utilities ($73 billion). The diagram by Statista shows the distribution of smart projects by segments.
Distribution of enterprise Internet of Things projects worldwide as of January 2018, by segment
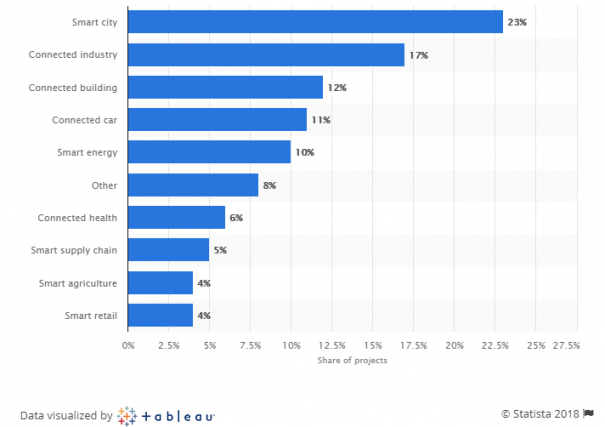
Source: Statista
6. At the Center of Cyberattacks

The core challenge for any digital transformation process is to provide absolute security. Unfortunately, the more complicated the IoT ecosystem gets, the more vulnerable it will be to cyberattacks. Hackers will continue to use connected devices to steal or damage private and commercial information.
In the coming decade, technology providers will have to focus more intensively on safety concerns. Their main goal will be developing efficient methods for fighting and, what’s more important, preventing hacking attacks.
Wrapping It Up
Nowadays, digitization is an indisputable blessing for any organization. Companies gain new values and insights into their assets on the basis of data and analytics.
The Internet of Things plays a crucial role in driving digital transformation and is a foundation for future smart businesses.
If you are in search of qualified IoT specialists or have any questions about hiring a dedicated team, do not hesitate to contact SaM Solutions.



























 5 Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce Application
5 Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce Application Using Salesforce to Improve Your Sales Pipeline: Five Tips
Using Salesforce to Improve Your Sales Pipeline: Five Tips Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Five Best Frameworks
Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Five Best Frameworks 10 Best Web Development Frameworks in 2023
10 Best Web Development Frameworks in 2023 How to Develop Custom Accounting Software
How to Develop Custom Accounting Software











 10 Best IoT Platforms for 2024
10 Best IoT Platforms for 2024 Top 20 Latest Trends in the Ecommerce Industry in 2024
Top 20 Latest Trends in the Ecommerce Industry in 2024 Top 10 Most Popular Programming Languages in 2024
Top 10 Most Popular Programming Languages in 2024 Digital Transformation Strategy [+ Key Trends in 2024]
Digital Transformation Strategy [+ Key Trends in 2024] How to Build Enterprise Software: The Ultimate Guide
How to Build Enterprise Software: The Ultimate Guide