It would be a mistake to think that sales strategies in all industries are identical because they have the same ultimate goal — to sell something. In reality, different goods should be sold in different ways, and therefore selling processes vary significantly. The eCommerce market is not homogenous. It consists of two main business marketing models — B2B and B2C. What are their differences and similarities? Read on to learn.
Request SaM Solutions’ ecommerce development services to grow your client base and boost profitability of your online sales.
Two Models: B2B vs. B2C eCommerce
B2B stands for Business-to-Business. This model facilitates relations and transactions between businesses, manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers through the Internet via an online enterprise platform. Processes are usually complicated because of the large volume of orders. An example of a B2B deal is selling tires to an automobile manufacturer.
B2C stands for Business-to-Consumer. This model describes relations between retailers and their customers and focuses on selling goods and services to end consumers directly via an online retail platform. Buying a T-shirt online or booking a plane ticket are vivid B2C examples.
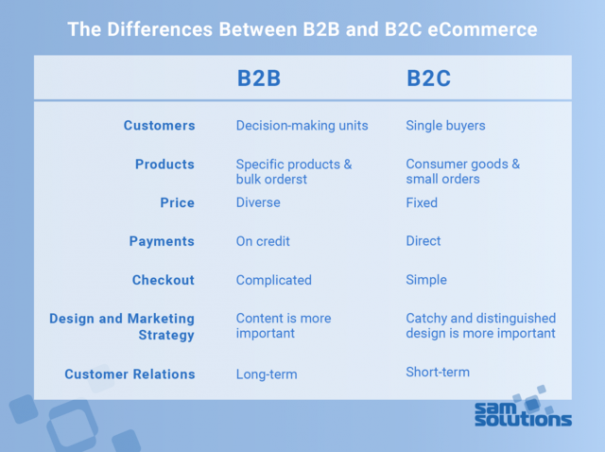
The Differences Between B2B and B2C eCommerce
There are many features that should be taken into account while developing an eCommerce system for your online store. The list below focuses on the main B2B and B2C differences.
Customers
The main point that differentiates two eCommerce approaches is the type of consumers they focus on. The difference between B2B and B2C customers is crucial.
B2B sites are geared toward large companies that acquire goods and services and later sell them to end users. Thus, B2B customers are decision-making units that may include managers, brokers, resellers, sales representatives, etc. They make logical and unemotional decisions based on business requirements and possibilities of the company. Since multiple people are involved in the purchase process, a lot of negotiations and customization is necessary from the initial contact until the moment the conversion process begins, and site visitors turn into paying customers.
B2C sites sell directly to individual users. B2C customers are single buyers searching for certain products for their personal needs or the needs of their relatives or friends. They often make decisions under the influence of emotions, likes and dislikes, and thus impulse buys are possible. B2C buyers don’t require an individual approach; they just need careful marketing and clear direction through the site to make the buying journey intuitive. The selling process is less labor-intensive for sellers.
B2C and B2B buyers purchase for absolutely different reasons and require different sales processes. Understanding your customer needs helps accurately tailor your eCommerce offerings.
Products
Another difference between B2B and B2C eCommerce lies in the type of products they sell.
B2B stores deal with specific products for enterprises, e.g. office furniture, chemical fertilizers or machinery parts for certain types of autos. In essence, they take a niche market and aim to satisfy the specific needs of their customers. Another B2B product feature is that business buyers usually need large quantities of products, so they make bulk orders.
B2C stores deal with a very broad market of consumer goods. A great example is the most popular online warehouse Amazon — it sells a huge variety of products, from toothbrushes and toys to TV sets and bicycles. Typical B2C users make small orders consisting of a single item or a couple of things.
Price
One more difference between B2C and B2B in eCommerce is price creation. Customer type and order volume predetermine product pricing. Within the B2B sector, prices are diverse. Sellers offer specific discounts depending on the number of products, delivery time or loyalty programs, so the price may rise or drop. Thus, B2B pricing policy is based on individual agreements between a store owner and a given company.
Within the B2C environment, all prices are fixed. Every client gets the same product catalog with a set price for every item. Each client’s previous purchasing relations with the store don’t influence the price. There may be discounts or special offers, but again, they are applied to all buyers equally.
Payments
Due to the fact that B2B clients tend to place high-volume orders or multiple orders in a short period of time, they prefer to pay on credit. It’s essential for B2B platforms to integrate with various transaction management solutions to provide their customers with different payment options, credit limits, payment history, etc. Post-delivery payment is a norm for business clients.
In B2C eCommerce, payments are more straightforward. Typically, buyers are expected to pay their orders directly, either using online methods or paying with cash to the delivery person.
Checkout
The B2B checkout process is complicated due to multiple orders, specific payment scenarios and delivery combinations. Online order confirmation or a chatbot is often not enough and live communication with sales team members is needed to clear all the details. Business clients prefer long-term relations and may repeat their orders, so having a unique account with saved details is likely to improve user experience and make reordering quick and easy.
B2C buyers prefer avoiding logins and registration. A simple checkout form that captures the basic information with the address details and delivery time is enough. Individual customers want a seamless purchasing journey through an intuitive website interface and without the need to talk on the phone with sales representatives.
Design and Marketing Strategy
B2B websites focus not so much on design (though it should be solid) as on the useful information their clients really need. The marketing strategy should emphasize professional customer service and aftercare to establish long-term relationships.
B2C sites must stand out from the rest because the competition in the consumer goods marketplace is tremendous. The website design should be catchy and distinguishable to attract as many clients as possible. The marketing strategy should also include alternative marketing channels, promotion via social networks, etc.
Customer Relations
B2B eCommerce is targeted at long-term relations with clients. Large businesses tend to reorder if they are satisfied with the services provided by a seller. The priority for a B2B vendor is therefore to retain buyers and build and maintain long-lasting partnerships.
B2C buyers are usually single visitors who are characterized by short-term relations with the online store. They focus on the purchase of the needed goods at the moment, and that’s it.
Similarities Between B2B vs. B2C eCommerce
The two eCommerce approaches are not complete opposites. B2C and B2B eCommerce similarities are:
- They are both sales processes and their ultimate goal is to sell something to clients
- Good customer service is crucial for success in both models
- Marketing strategy is a must for both
- Multi-channel promotion is beneficial for both (YouTube, Facebook, LinkedIn)
Finally, the most obvious similarity is that on both sides of these two eCommerce models are people. Relationships between people based on trade have been developing for centuries. Now, their external appearance has changed, but the essence remains the same.
Wrapping It Up
There is not just one difference between B2C and B2B in eCommerce. Many features differentiate these models. If a company plans to create an online-trading solution, a number of unique requirements should be taken into account to fit with customer requirements perfectly.
SaM Solutions has vast eCommerce expertise and helps large and small retailers improve their online shopping experience. We work with the leading platforms SAP and Magento. Contact us to build your online shop!



























 5 Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce Application
5 Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce Application Using Salesforce to Improve Your Sales Pipeline: Five Tips
Using Salesforce to Improve Your Sales Pipeline: Five Tips Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Five Best Frameworks
Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Five Best Frameworks How to Develop Custom Accounting Software
How to Develop Custom Accounting Software 10 Best Web Development Frameworks in 2023
10 Best Web Development Frameworks in 2023


![What Is Ecommerce Customer Service? [Including 8 Best Practices]](https://www.sam-solutions.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/Customer-Service-in-eCommerce.png)








